Table of Contents
Psychological Models of Empathy
Part of Project Lirec: Notes from “Concepts and Evaluation of Psychological Models of Empathy” (Extended Abstract), Enz. S., Zoll, C., Diruf, M., Proc. 8th Int. Conf. on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems (AAMAS 2009), Decker, Sichman, Sierra, and Castelfranchi (eds.), May, 10– 2009, Budapest, Hungary, pp. XXX-XXX. http://lirec.eu/biblio/1703
Types of Empathy
- Cognitive empathy - an understanding of other's internal state
- Affective empathy - includes the emotional reaction to other's internal state
Emotional Contagion
Affective empathy can come from cognitive empathy, but can also come from direct transfer of emotions - “emotional contagion”. This is important for social identity and group dynamics - eg. a herd needing to react quickly to the presence of a predator, which may only be spotted by a few individuals.
Emotional contagion may result in different immediate responses in more complex situations, such as 'gloating'.
Empathic processes
The separation of empathy into cognition and it's results are important because the outcomes can also be seen as the result of other processes.
Non-cognitive processes
- Pre-verbal links
- Early in life - babies cry in presence of other crying babies.
- Motor mimicry, simply following other's gestures creates an emotional link - also used later in life.
Simple cognitive processes
- 'Classical conditioning' sharing an intense emotional experience with another person, allows you to learn the connection between responses and situations. Later you can relate a similar response in another person with the event you've experienced.
- Internal labeling of situations with appropriate responses.
Advanced cognitive processes
- Language understanding (even alone, in situations like engaging with characters in a book)
- 'Role taking' - imagining yourself in another's perspective.
All these can operate simultaneously.
Intrapersonal outcomes
- Internal changes, expressed or not
- Affective outcomes
- Parallel - same emotion, motor mimicry
- Reactive - merge own with other's reactions (distress, sympathy or gloating).
Accuracy of understanding is determined by:
- Similarity and familiarity with subject
- Difference between explaining your own behaviours and others (tend to be situational forces vs personality characteristics)
Interpersonal outcomes
Changes in behavior resulting from empathic processes:
- Helping
- Aggression
- Social behavior
OCC Theory
Used as the basis of FAtiMA
- Appraisal of events → Emotions
- Appraisals can be checked and are learned over time
Appraisals are carried out on:
- Objects regarding their appealingness
- Agents regarding the praiseworthyness of their actions
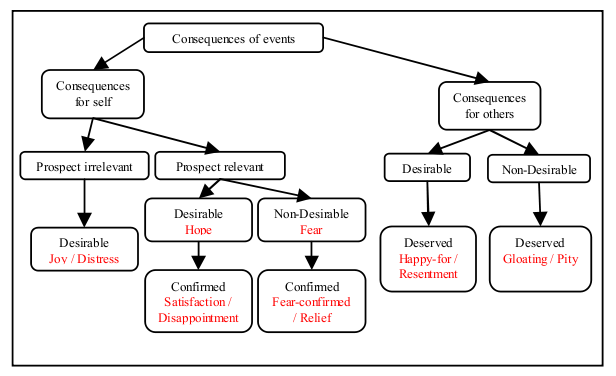
- Outcomes of events regarding their desirability, for the agent itself, or for others.
The OCC model has a set of emotional categories:
- Fortunes of others: Happy-For, Resentment, Gloating, Pity
- Prospect based: Satisfaction, Relief, Fear-confirmed, Disappointment
- Well being: Joy, Distress
- Attribution: Pride, Shame, Admiration, Reproach
- Well being/Attribution compounds: Gratification, Gratitude, Remorse, Anger
- Attraction: Love, Hate
The five phases of emotion processing
1. Classification: Event, action or object, according to emotional cateories 2. Quantification: What are the intensities? 3. Interaction: With the current emotional categories of the agent 4. Mapping: 22 emotional categories to lower number of emotional expressions 5. Expression: face expression etc.